Scientific Research involves performing a methodical study to prove a theory or answer a specific question. It is carried out in Universities, Laboratories and Hospitals across Ireland by healthcare professionals and scientists. Examples of questions that have been addressed by research into diabetes are:
- Will good glucose control delay retinopathy cataracts, neuropathy etc?
- What are the optimal treatment targets for glucose, blood pressure and cholesterol in type 2 diabetes?
- How does drug “x” compare against weight loss, dietary change, and exercise?
Research involves gathering numbers, statistics, opinions, motivations, and observations to answer these kinds of questions.
How will you know “health claims” are true?
Research becomes valid information when it is shared with peers, discussed, disputed, and tested by other scientists. Research teams look to publish their findings in reputable medical journals. Published research brings recognition that helps scientists raise funds to do more research.
Types of Research
There are two types of research: quantitative research which deals with numbers and qualitative which deals with attitudes, opinions, and behaviour.
Quantitative Research is used to quantify a problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into usable statistics. It is used to quantify attitudes, opinions, behaviours, and other defined variables and generalise results from a larger sample population. Quantitative Research uses measurable data to formulate facts and uncover patterns in research. Quantitative data collection methods are very structured and data collection methods include various forms of surveys – online surveys, paper surveys, face-to-face and telephone interviews, online polls, and systematic observations.
Qualitative Research is primarily exploratory research. It is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations to provide insights into a problem or to further develop ideas or hypotheses for further research. Qualitative Research is also used to uncover trends in thought and opinions. Common data collection methods include focus groups (group discussions), individual interviews, and participation/observations. The sample size is typically small, and respondents are selected to fulfil a given quota.
If you would like to read more on research terminology, visit IPPOSI clinical trials. Please note that clinical trials.ie is a public awareness initiative created by IPPOSI (Irish Platform for Patient Organisations, Science & Industry)
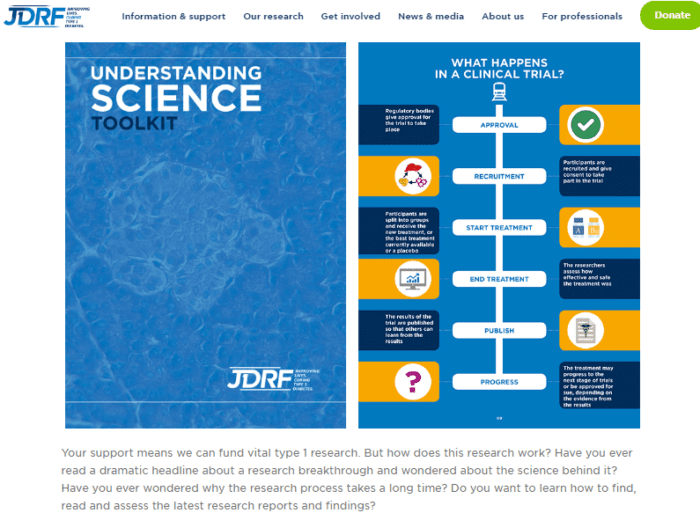
Clinical Trials
Research on medications, devices and treatments has to undergo animal and/or human clinical trials to protect the health of the population.
What is a breakthrough in Research?
Many new advances in diabetes management are heralded as a dramatic breakthrough by the media whilst in reality, the study is still ongoing with potential side-effects and effectiveness being carefully monitored. When you hear of a breakthrough in diabetes, visit the Diabetes Ireland website for official news releases and interpretation of new findings.
Phases of Clinical Trials
Before drugs and certain treatments come onto the public market, they must undergo clinical trials. There are 3 to 4 phases that a company has to undertake. The table below gives you an idea of how much work is involved in this process.| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial Duration | 4 years | 18 months | 2 to 15+ years | 2 -10 years |
| Number of People Involved | 10 to 20 | Hundreds of people | Thousands of people | A selection of patients using the device/medication/ treatment |
| Health Status of Participants | Healthy people | People diagnosed with the condition | People diagnosed with the condition | People diagnosed with the disease/condition using the drug/treatment as prescribed |
| What happens at each Phase | Safety test | Several trials to test the safety and effectiveness of the product/intervention | Expand trials to all ages with all stages of the condition. Possibly randomised controlled trials using placebo and the real treatment. Application for license to market. Trial results usually appear in media at this stage | Trials continue while treatment is publicly available for safety surveillance & drug technical support. |
Clinical Trials & Diabetes
The biggest practical questions in the management of diabetes are first, how to avoid it? And second, how to assure the best possible future for those who develop the condition? Landmark Clinical Trials are DCCT/EDIC. (Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications) in Type 1 Diabetes and UKPDS (United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study) in Type 2 Diabetes.
JDRF
For more information on interpreting medical research and clinical trials, please click on the link below.